South Africa
South Africa
Official Name: Republic of South Africa
Capital: Pretoria (executive), Bloemfontein (judical) and Cape Town
(legislative)
Independence Day: 27 April 1994
Currency: South African Rand (ZAR)
Key Result
15,000 women and youth reached through four community-based projects implemented focused on drug rehabilitation, gender-based violence and skills development.
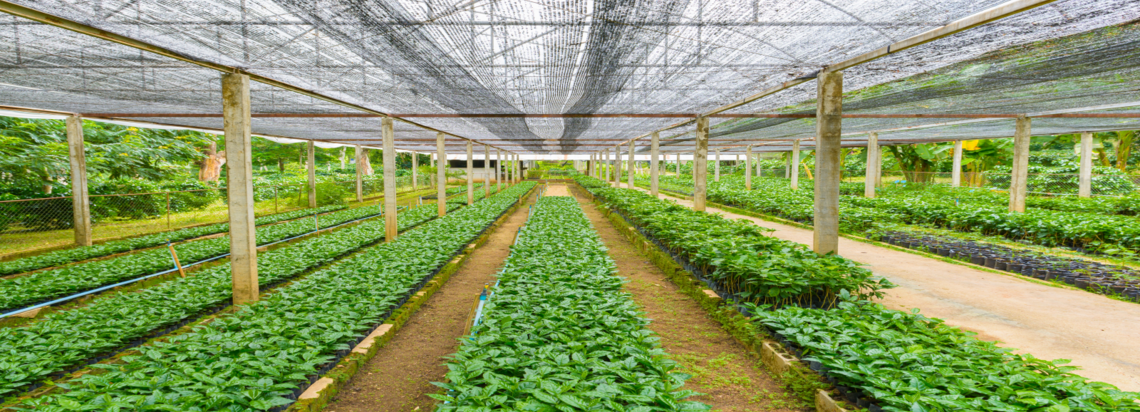
The Skills Initiative for Africa (SIFA) set up a financing facility to support innovative vocational training initiatives in South Africa.
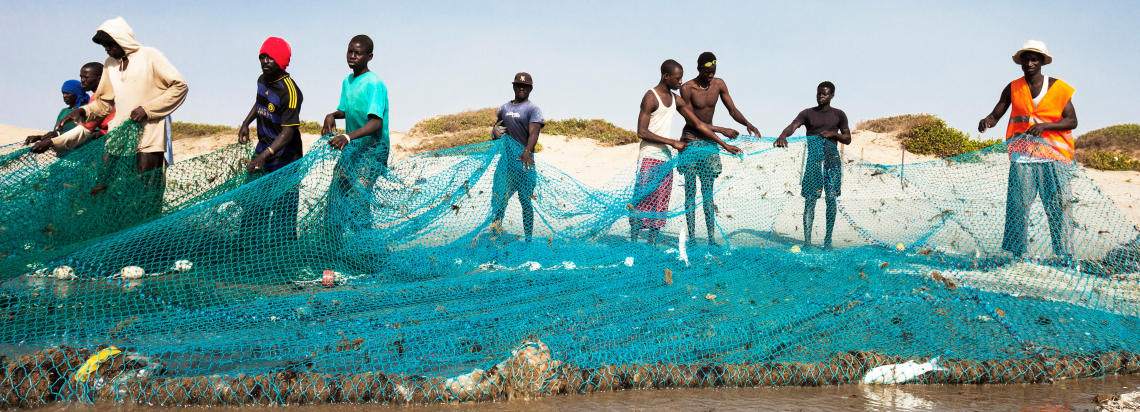
More than 500 small scale livestock farmers on how to plant, process and use Tephrosia bio-acaricide have been trained with support of local leadership.
Sensitised Government officials to incorporate the Home-Grown School Feeding (HGSF) model into existing school feeding programmes, to ensure that school meals are locally sourced through a continent-wide mapping and experience sharing exercise.
85 Million hectares of land on the continent have been committed for restoration through the application of the restoration opportunities assessment methodology by 2030. South Africa committed 3.6 million hectares.
700 traditional council members committed to mainstream climate change in agriculture in their communities, based on A Provincial Early Action Strategy (REAS) documented and disseminated for the Kwa-Zulu Natal Province. Furthermore, the strategy was translated into the local language IsiZulu and disseminated to 1200 change agents.
Related
Projects

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

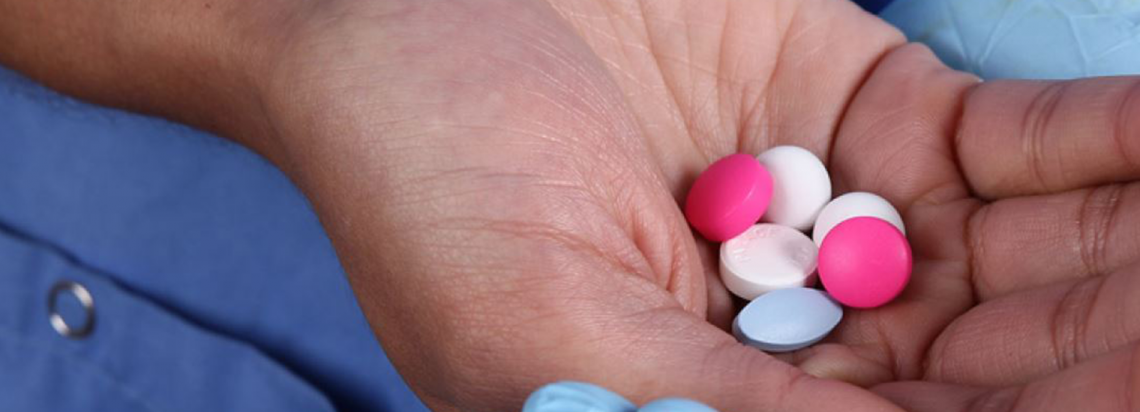
A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.
A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.
A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in South Africa.
South Africa has a registered RCORE specialized in quality assurance and quality control of medicines called North West University (NWU) – Potchefstroom Campus, South Africa – WHO Collaborating Centre for the Quality Assurance of Medicines. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.
you agree to the AUDA-NEPAD Privacy Policy.