 Tanzania
Tanzania
Official Name: United Republic of Tanzania
Capital: Dar es Salaam
Independence Day: 9 December 1961
Currency: Tanzanian shilling (TZS)
Key Result
Tanzania received USD22.9 million from the Global Agriculture and Food Security Programme (GAFSP) to support the rehabilitation of irrigation schemes and an input voucher scheme for rice input packages in the project zones.
Tanzania received support from the TerrAfrica Leverage Fund to the tune of USD100,000 for its project on Greater Serengeti Sustainable Landscape Management Information System.
Fisheries sectorial policies, governance reviews, and economic profiles were conducted and the review reports formally presented to Ministers of Fisheries and of Finance.
In 2017, training on bio-equivalence was conducted by Tanzania Food and Drugs Authority in collaboration with Muhimbili University.
The Dar es Salaam Port Expansion (DFS) project aims to increase cargo throughput; handle larger vessels in the container, liquid and dry bulk trades; improve interfaces across transport modes; improve linkage services with rail services.
Related
Projects

A critical AU Model Law aimed at harmonizing medical products regulatory systems in Africa was endorsed by African Heads of State and Government at the January 2016 AU Summit in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The AU Model Law will contribute towards accelerate the regulation of safe, quality and affordable medical products and technologies in Tanzania.
The Headquarters of the East African Community (EAC) is in Arusha Tanzania. In 2012, the EAC Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (MRH) programme was established and Tanzania participated in the development and subsequent adoption of harmonized technical guidelines by the EAC Council in 2014 and publication of a compendium for EAC member states. Two pilot projects: the World Health Organization Medicines Prequalification Program (WHO-PQP) and the EAC Joint Assessments and Inspections ensured that Tanzania participated in the approval of 5 and 7 products in 2011 and 2013 respectively. Phase two of the EAC-MRH programme has expanded to include drug safety (pharmacovigilance) strengthening; clinical trials oversight; regulation and quality assurance of medical devices including diagnostics; and harmonization of regulation of vaccines.
There are two (2) NMRAs participating on the MRH programme in Tanzania, namely the Tanzania Food and Drugs Authority (TFDA) and the Zanzibar Food and Drugs Board. In 2015, the EAC-MRH programme conducted a Joint Dossier Assessment of 8 medicinal products in Entebbe, Uganda. As a result, Tanzania granted conditional approval of four (4) products.
Tanzania has two designated RCOREs specialized in training in core regulatory functions and medicine evaluation and registration namely: St. Luke’s Foundation, Tanzania – Kilimanjaro School of Pharmacy; and School of Pharmacy, Muhimbili University of Health and Allied Sciences (MUHAS) – Tanzania Food and Drugs Authority (TFDA) respectively. RCOREs are institutions with specific academic and technical regulatory science expertise and training capabilities capable of producing regulatory workforce in Africa.

Mainstreaming nutrition in National Agriculture and Food Security Investment Plans (NAFSIPs) in Africa While many CAADP NAfSIPs include nutritional goals, most are lacking the concrete actions needed to ensure nutrition security. This gap is being addressed by NEPAD’s initiative to strengthen capacity for addressing nutrition in the formulation and implementation of NAfSIPs. The NEPAD Agency held sub-regional workshops in Botswana to ensure that agricultural and economic development policies and initiatives are nutrition-sensitive and have a clear approach, stronger capacities and clear road maps for implementation.

CAADP Compact: Tanzania signed the CAADP Compact on 6 - 8 July 2010.
Capacity Building: NEPAD supported Tanzania in conducting an Independent Technical Review (ITR) from 20 – 31 May 2011.
National Agriculture Investment Plan: Tanzania is now in advanced stages of implementing NAIP. Tanzania also received support on undertaking a joint agriculture review and public expenditure study. A capacity assessment was undertaken as well.
Business: First CAADP Business Meeting was held on 9 - 10 November 2011.
Funding: Tanzania received funding from the Global Agriculture and Food Security Programme (GAFSP) amounting to USD 22.9 million.


Project : TAH programme
Description : This is phase I of the continental connectivity programme that focuses on completion and standardisation of the TAH missing links by 2030
Project : Single African Sky phase 1 (design and initial implementation)
Description : Single African Sky is a continental programme that will create a high-level, satellite-based air navigation system for the African continent
Project : Yamoussoukro Decision implementation
Description : Accelerate Yamoussoukro Decision implementation by identifying countries that are ready to fully implement it, and discussing and agreeing with both their governments and airlines to launch the voluntary club on a full membership basis;
Project : ICT Enabling Environment
Description : This programme would improve the environment for the private sectors to invest in high-speed broadband infrastructure
Project : ICT Terrestrial for Connectivity
Description : This programme has two main components: secure each country connection by at least two broadband infrastructure and ensure the access to submarine cable to all landlocked countries
Project : Internet Exchange Point (IXP) programme
Description : The aim of this programme is to provide Africa with adequate internet node exchange to maximise internal traffic
Project : Rusumo Falls
Description : Hydropower production of 61 MW for Burundi, Rwanda and Tanzania
Project : Central Corridor
Description : This programme would modernize the third priority ARTIN corridor in East Africa and facilitate travel for people and goods across the borders between Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi and DRC
Project : Dar es Salaam Port Expansion (DFS)
Description : To increase cargo throughput; handle larger vessels in the container, liquid and dry bulk trades; improve interfaces across transport modes; improve linkage services with rail services
Project : Zambia-Tanzania-Kenya Transmission Line (DFS)
Description : Promoting power interconnection across the continent and facilitating the creation of a Pan African power market.



Technical capacities were strengthened to establish and manage functional biosafety systems for the safe use of modern agricultural biotechnology. Other technical support included national biosafety training workshops, biosafety short courses at African institutions and partner institutions outside Africa, notably at Michigan State University in the USA, biosafety internships, technical consultation support, and biosafety information resources.
Biosafety short courses form an integral component of ABNE activities in Africa. In 2014, ABNE presented a biosafety short course at Makerere University in Uganda and agricultural biotechnology short courses at Michigan State University in the USA. A total of 24 regulators drawn from Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, Uganda and Zimbabwe gained broad insights into the basics of biosafety science, policy and regulation, GM crop risk assessment and management, and biosafety communication and awareness creation.
Through high-level policy dialogue, ABNE has also supported Tanzania to fast track the process of establishing functional biosafety mechanisms.
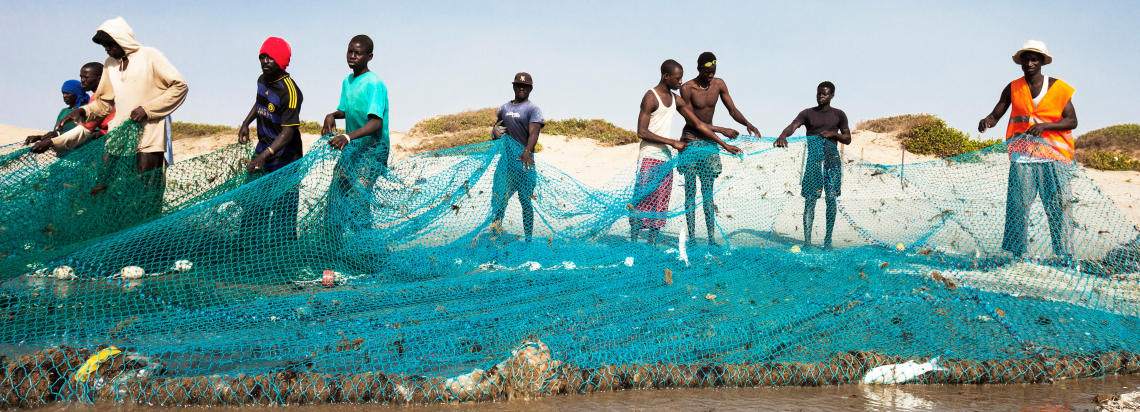

The Fisheries Improvement Programme of the Fisheries and Aquaculture Programme which assists countries to receive certification for their products facilitated certification efforts in Tanzania. All the required steps were taken and the certification process for fisheries of octopus in Tanzania is in progress.
Project Name: Empowerment of African Women - Graca Machel Trust Fund (GMT) -Promotion of Women’s Rights


The Fund supported the alignment of the gender sensitive CSA to the country's NDP.

The ASTII project was introduced in the country in September 2007. Consequently, data collection surveys were held and both R&D and Innovation survey core indicators-data featured in the 1st African Innovation Outlook (AIO-2010) as well as in the second report (AIO-2014).
Tanzania had an in-country training workshop in 2015, and as well participated in ASTII regional workshops jointly coordinated by NEPAD, the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, the South Africa’s Centre for Science, Technology and Innovation Indicators (CeSTII), and the Research Policy Institute of the University of Lund, held between 2008 and 2012 on international survey methodologies (OECD).
An investment of about USD175,000 was made for surveys carried out in 2014 and 2015. Furthermore, the country received almost USD50,000 during the 1st phase of ASTII (2007-2010) from SIDA as a seed grant.
Contact: Dr Mafunda (dmafunda@costech.or.tz), Dr Festo Mario (fmaro@costech.or.tz; marofesto@gmail.com) and Mrs. Blandina Mkayula (bmkayula@gmail.com; bmkayula@msthe.go.tz).
Website: http://www.costech.or.tz

Results (2013 – 2015)
Advocacy and Strengthening of Negotiation Capacities on Post-2015 Development Agenda through the Common African Position (CAP):
• The multi-stakeholder framework of engagement specifically enhanced dialogue towards ensuring the required mass to influence the Post-2015 Global Agenda and Development Goals relevant to the Continent;
• This intervention helped strengthen country and regional level negotiating capacities for the effective incorporation and articulation of Africa’s priorities as enshrined in CAP in the final Global SDGs;
• The project enabled the participation of African stakeholders at the Means of Implementation Engagement, 3rd Financing for Development Conference and the UN General Assembly that adopted the new SDGs. This ensured the incorporation of Africa’s development priorities into the new goals through developing essential negotiation capacities;
• Through the CAP/SDGs space on the Africa Platform for Development Effectiveness (APDev), knowledge products and negotiation documents, as well as, policy briefs where successfully disseminated to the African negotiators in New York and kept the continent’s stakeholders informed of the overall process;
• Development and dissemination of post-2015 Policy Briefs on “Financing and Partnerships” and “Structural Economic Transformation and Inclusive Growth”. These are priorities outlined in the CAP and the policy briefs where utilized in the negotiation process for the African continent.
Global Partnership for Effective Development Cooperation (GPEDC):
• Africa secured the hosting of the 2nd High Level Meeting (HLM) of the Global Partnership. This was attained through robust negotiation and facilitating a common voice from Africa with regards to this critical engagement by the NEPAD Agency. The 2nd HLM will be held in Nairobi Kenya;
• The NEPAD Agency advocated for the full inclusion and participation of Africa’s Regional Economic Communities (RECs) in conducting the 2nd GP Monitoring Exercise. This was a fundamental achievement considering the RECs are the continent’s building blocks with regards to socio-economic transformation;
• The Africa Action Plan on Development Effectiveness (AAP) was granted the status of an official Global Partnership Initiative (GPI) at the Planning Meeting in Brussels. The AAP was developed by the NEPAD Agency in consultation with African multi stakeholders. This has enabled the Agency to successfully mobilize resources towards the implementation of the AAP.
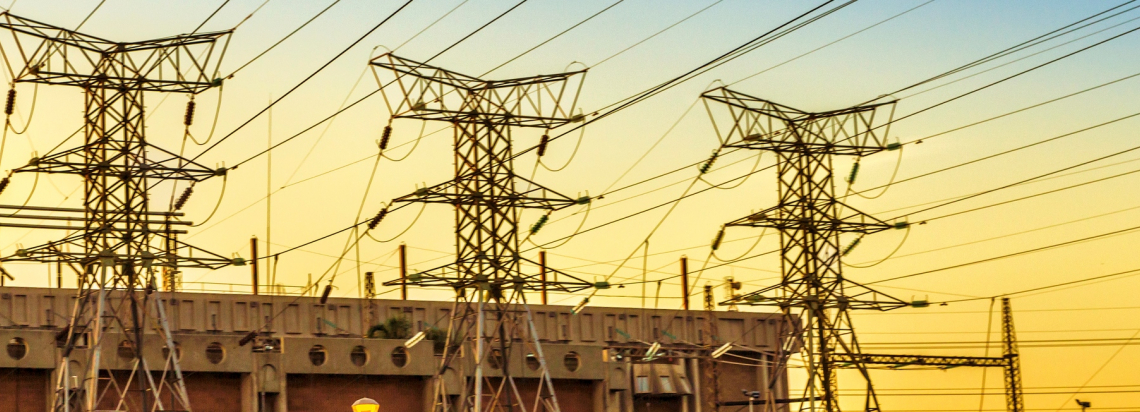

Project : Transmission – Zambia-Tanzania-Kenya Transmission Line Project
Countries/Region : Zambia, Tanzania and Kenya | East and Southern Africa regions
Project Location : Kabwe (Zambia) through Mbeya (Tanzania) to Isinya (Kenya) via Iringa, Singida and Arusha (all in Tanzania)
Sector/Subsector : Energy/Transmission
Project Description : Construction of a transmission line that will connect the Zambian grid to Kenya, via Tanzania, covering a distance of 2,200 km.
Project : Transmission-- North South Transmission Line Project
Countries/Region : Egypt, Sudan, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi,Mozambique, Zambia, Zimbabwe, South Africa, | East and Southern Africa
Project Location : Regional Interconnector-East and Southern Africa
Sector/Subsector : Energy/Transmission
Project Description : Construction of an 8,000 km, 3,000 - 17,000 MW capacity transmission line system from Egypt through Sudan, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe to South Africa, connecting the Eastern Africa Power Pool (EAPP) and the SAPP.

Project : North-South Corridor Road/Rail Project
Description : Construction of a multi-modal trans-continental interconnector
Estimated total cost : N/A. Cost is based on the specific project within the corridor
Description : The use of political gravitas and goodwill to unblock and facilitate political bottlenecks affecting the implementation of ICT broadband and optic fibre projects on the continent


New Alliance for Food security and Nutrition and Grow Africa Partnerships: 36 LOIs from 20 domestic companies and 16
international.
• $4,465,425,000 of planned investment.
• $529,769,143 reported as invested in 2014,
making a cumulative total of $1,141,285,809 to
date.
• 850,350 smallholders reached in 2014
• 4,240 jobs created in 2014.
• $128 million donor disbursements in 2014 (62%
of expected).

Tanzania has received support from the TerrAfrica leveraging Fund (TLF) to the tune of $100,000 for its project on “GREATER SERENGETI SUSTAINABLE LANDSCAPE MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM”.

At the beginning of 2014, 37 of the 42 opted-in African countries have completed a rapid assessment / gap analysis. The next step for countries is to develop a SE4LL Action Agenda and Investment Prospectus(es). To support this process, the SE4ALL Africa Hub partners have led the development of Africa Guidelines for SE4ALL national Action Agendas. The Africa Guidelines lay out principles and process for developing Action Agendas and put forward a balanced approach of centralized and decentralized solutions to achieve universal access to energy services.
Progress in Tanzania:
Starting SE4All Action Agenda and SE4All Investment Prospectus are under development"
Project: AIMS- Tanzania
Decsription: AIMS-Tanzania is being launched as part of the AIMS Next Einstein Initiative (AIMS-NEI), a coordinated programme to launch 15 AIMS centres across the continent. This ambitious plan has won support from the Governments of Cameroon, Ghana, Sénégal, South Africa, the United Kingdom, Germany and Canada, and has been awarded the TED Prize in 2008; the 2010 WISE Award, the 2012 UNESCO-Hamdan Prize for Outstanding Practice and Performance in Enhancing the Effectiveness of Teachers; and the 2008 Google Project 10^100 competition, selected as one of 5 winners out of 150,000 entries.
Overall Project Results:
AIMS is already making a big difference: since 2003, 731 students – 30% of them women – from 41 African countries have graduated from AIMS. Over 80% have gone into Master's and PhD programs directly after AIMS at excellent universities in Africa and abroad. AIMS graduates are now strengthening African universities, research centers, government and industry. For example, many of the mathematics lecturers at the Universities of Zambia and Khartoum are AIMS graduates and are now in turn educating hundreds of students each year. Among the AIMS graduates: 55 have completed PhDs, 233 completed Research Master’s, and many more are in the process of completing similar post-graduate programs.
you agree to the AUDA-NEPAD Privacy Policy.




